In the National Health Service there are 1,000 structures that provide hospital assistance, 8,867 for specialist outpatient assistance, 7,372 for residential territorial assistance, 3,086 for semi-residential territorial assistance, 5,586 for other territorial assistance and 1,122 for rehabilitation assistance (those to which article 26 of Law 833/78 refers).
The structures that provide hospital assistance and those that provide other territorial assistance are mostly public (respectively, 51.8% and 87.0%). On the other hand, the structures providing residential (82.3%) and semi-residential (68.6%) territorial assistance and the structures that provide rehabilitation assistance (77.9%) are accredited mostly private.
These are some of the data highlighted in theStatistical yearbook of the national health service - year 2017, created by the Statistics Office of the Ministry of Health. The publication presents statistical data on 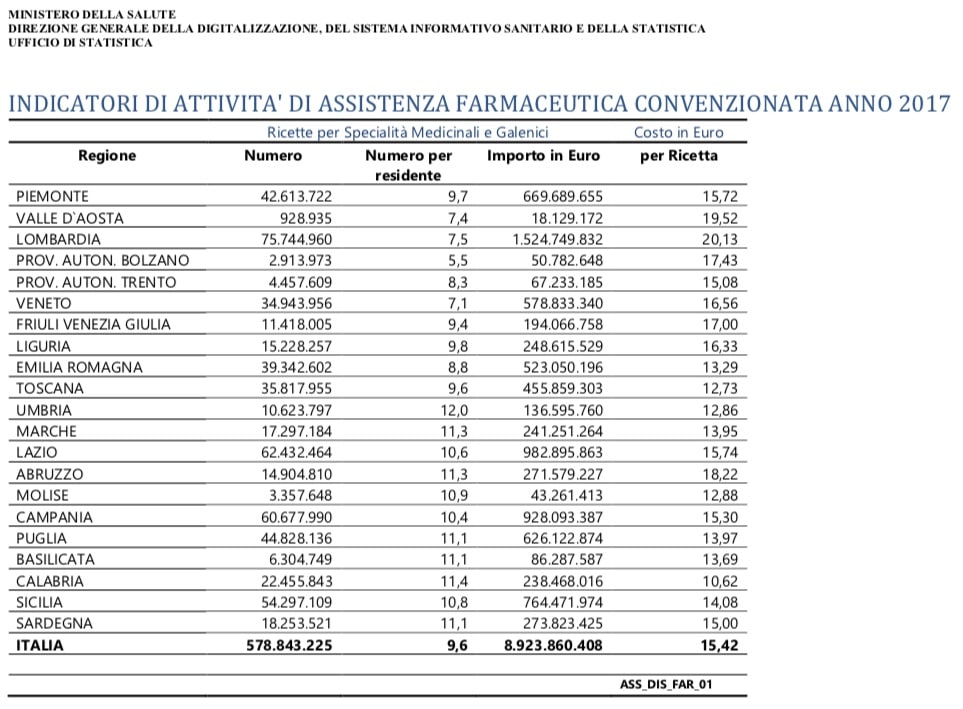 structures of the healthcare offer network and connected services, organizational characteristics, production factors and data on territorial and hospital assistance activities. The information is processed on the basis of the information flows detected on the basis of the Ministerial Decree of 5 December 2006 "Variation of the data collection models of the management activities of health structures", which regulates the transmission of data from Regions and autonomous Provinces to the Ministry of Health.
structures of the healthcare offer network and connected services, organizational characteristics, production factors and data on territorial and hospital assistance activities. The information is processed on the basis of the information flows detected on the basis of the Ministerial Decree of 5 December 2006 "Variation of the data collection models of the management activities of health structures", which regulates the transmission of data from Regions and autonomous Provinces to the Ministry of Health.
Supply network structures, the trend
The analysis of the data in the period 2014-2017 still shows a decreasing trend in the number of hospitalization structures, due to the rationalization interventions of the hospital networks which determine the reconversion and unification of many structures: the number of public structures decreases by 2.0%, that of accredited private structures decreases by 1.7%.
For specialist outpatient assistance, there is a substantial decrease in public outpatient clinics and laboratories (1.7%) and a slighter decrease for accredited private structures (0.2%).
Diverging trends can be seen between public providers and accredited private providers of residential territorial assistance (-3.6% for the public, +2.9% for the accredited private sector).
For semi-residential territorial assistance, the increase in structures is mainly attributable to accredited private providers for which, in the time period in question, there was an increase of 2.5%.
An increase in accredited private structures (1.8%) was also observed in the field of rehabilitation assistance pursuant to article 26 of Law 833/78.
Lastly, for the assistance provided by other local structures, there was a decrease of 0.6% for public structures and an increase of 1.4% for accredited private structures.
District assistance numbers
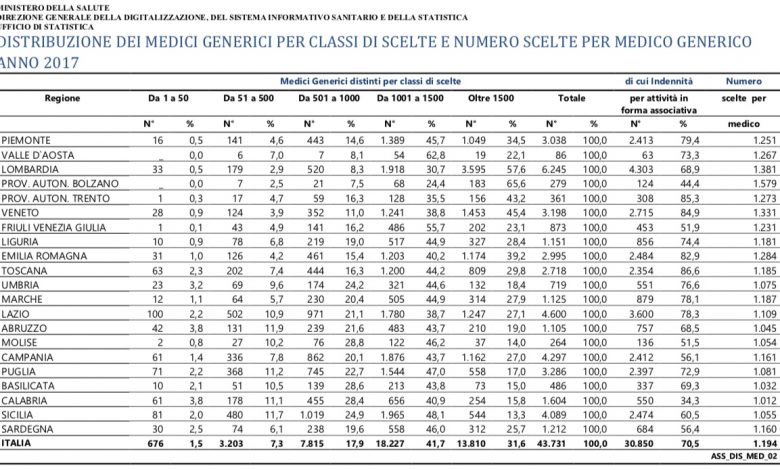
On average, nationwide each general practitioner has a potential workload of 1,211 resident adults. At the regional level there are significant differences:
- for the Northern Regions, with some exceptions, the deviations from the national average are positive. In particular, the Autonomous Province of Bolzano is highlighted with 1,613 adult residents per general practitioner (note that in the Autonomous Province the agreement with the NHS for general practitioners establishes a maximum number of choices of 2,000 patients)
- in all the Southern Regions, with the exception of the Sardinia Region, the potential burden of general practitioners is lower than the national average value; the Basilicata Region, in particular, records the minimum value of 1,037 adult residents per doctor.
The average potential burden per pediatrician nationwide is 989 children, with a wide territorial variability (from a value of 862 children per pediatrician in Sicily to 1,236 children per pediatrician in the Autonomous Province of Bolzano). However, all Regions are characterized by a more or less accentuated shortage of paediatricians in agreement with the NHS.
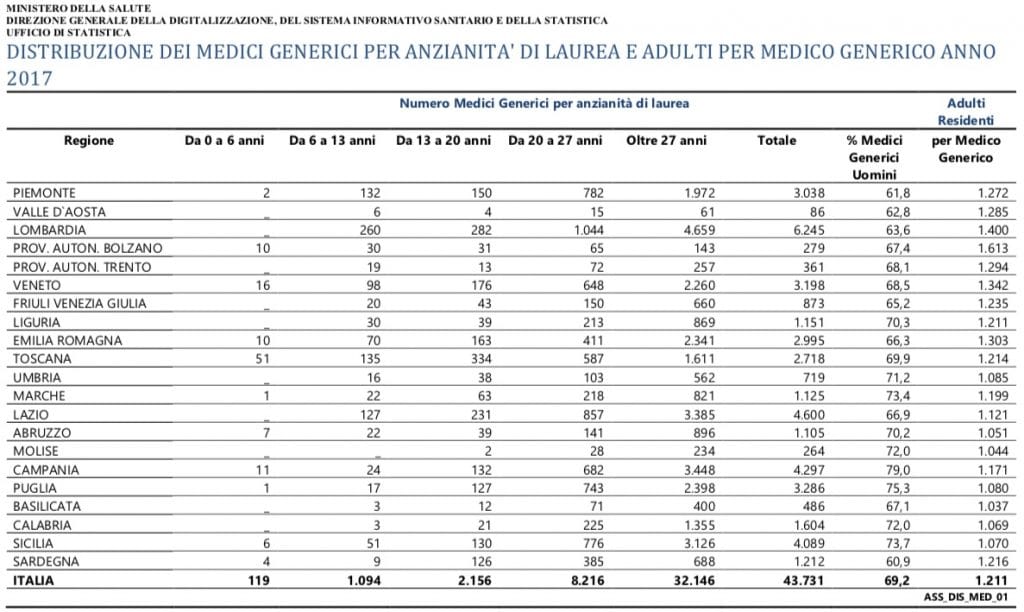 Given the potential burden of general practitioners (general practitioners and paediatricians), it is possible to evaluate the actual care burden, given by the number of members of the NHS (those who have chosen their general practitioner from the competent ASL) for each doctor.
Given the potential burden of general practitioners (general practitioners and paediatricians), it is possible to evaluate the actual care burden, given by the number of members of the NHS (those who have chosen their general practitioner from the competent ASL) for each doctor.
In 2017 they were detected in Italy 3,063 emergency medical points; with 11,688 registered doctors or 19 doctors for every 100,000 inhabitants. At the territorial level there is a remarkably diversified reality both in terms of the density of emergency medical points and in terms of the number of doctors in charge for every 100,000 inhabitants.
In Italy in 2017 they were prescribed 578,843,225 prescriptions with an amount of around 9 billion euros, with an average cost per recipe of 15.42 euros. The average cost per recipe is highly variable within the national territory, recording the minimum value in Tuscany (12.73 euros) and the maximum (20.13 euros) in Lombardy.
During 2017 they were assisted at home 1,014,626 patients; of these, 83.7% is represented by assisted patients aged 65 or over and 8.8% is represented by terminally ill patients.
Hospitalization and care facilities
In 2017, the SSN has approx 191,000 beds for ordinary hospitalization, 13,050 day hospital places, And 8,515 places for day surgery. Nationwide they are available 3.6 beds for every 1,000 inhabitants; in particular, the number of beds dedicated to acute care activities is 3.0 for every 1,000 inhabitants.
The presence of technical-biomedical equipment (in hospital and territorial structures) is increasing in the public sector, but availability is highly variable at the regional level. There are approx 96.9 mammograms for every 1,000,000 inhabitants, with values over 150 in two Regions (Valle d'Aosta, Umbria).
Particular interest has been held in recent years by theemergency area: 55.0% of public hospitals are equipped with an emergency department and over half of all institutions (65.4%) with a resuscitation centre. The emergency department is present in 79.9% of hospitals. The pediatric emergency room is present in 17,4% of hospitals.





